The washing machine is one of the most used appliances in your home. It’s also one of the most expensive appliances to repair and replace.
In this blog post, we’ll take a look at how an ac capacitor can help reduce repair costs and improve the quality of your washing machine.
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor is essentially an electrical storage device that stores energy when it is charged. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator known as a dielectric material. The plates are made from aluminum or copper, while the dielectric material is usually plastic or ceramic.
How Is a Capacitor Used in a Washing Machine?
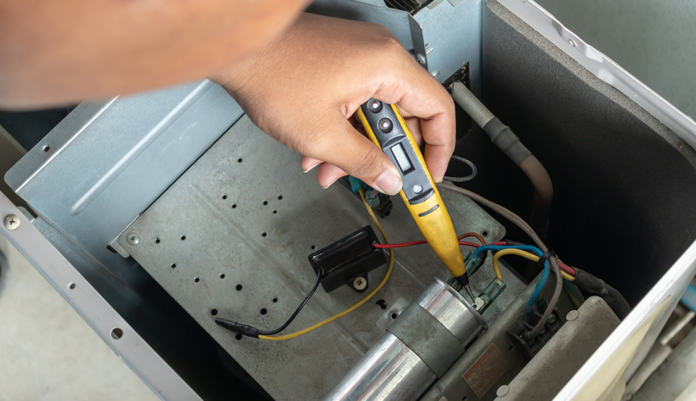
Capacitors are used in washing machines to control motor speed. It also acts as a power source for the motor. It has to be replaced every time it fails.
The capacitors in a washing machine are located near the back of the unit, close to where the power cord and water supply line connection. If you have an older model, the capacitor may be in a separate housing and mounted on top of or behind the machine.
When capacitors fail, they can cause your washer to stop working altogether, or not work at full capacity. Depending on how old your washer is and how often you use it, you may need to replace capacitors every few years or even more frequently.
Is the Capacitor Important in Washing Machine?
If you have an older washing machine, it may have been fitted with a capacitor that has failed due to age or wear and tear over time. There are many different types of capacitors available but they all serve one main function: to store energy in order to supply power for other components within your appliance such as motors, heating elements and lights etc… If your washing machine does not have a capacitor fitted then it will not be able to run properly or at all!
Why do Capacitors in Washing Machines Fail?
When a washing machine capacitor fails, the motor will not run. This is due to the fact that the capacitor stores energy and distributes it to the motor.
Corrosion – The most common cause of failure is corrosion on the contacts inside the capacitor. When this happens, it results in an open circuit which means that there is no flow of current between them.
This will cause your washing machine to stop working because it cannot generate enough power to spin at full speed or even turn on at all.
Heat – The heat generated by the motor can cause the dielectric fluid inside of the capacitor to evaporate. Once this happens, it will no longer be able to store electricity properly and can cause sparks or even a fire if not detected quickly enough!
Age – As capacitors age, they become less resistant to heat and voltage changes — which in turn causes them to fail prematurely.
Conclusion
The washing machine is one of the most used appliances in your home. It’s also one of the most expensive appliances to repair and replace.
In this blog post, we’ll take a look at how an ac capacitor can help reduce repair costs and improve the quality of your washing machine.
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor is essentially an electrical storage device that stores energy when it is charged. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator known as a dielectric material. The plates are made from aluminum or copper, while the dielectric material is usually plastic or ceramic.
How Is a Capacitor Used in a Washing Machine?
Capacitors are used in washing machines to control motor speed. It also acts as a power source for the motor. It has to be replaced every time it fails.
The capacitors in a washing machine are located near the back of the unit, close to where the power cord and water supply line connection. If you have an older model, the capacitor may be in a separate housing and mounted on top of or behind the machine.
When capacitors fail, they can cause your washer to stop working altogether, or not work at full capacity. Depending on how old your washer is and how often you use it, you may need to replace capacitors every few years or even more frequently.
Is the Capacitor Important in Washing Machine?
If you have an older washing machine, it may have been fitted with a capacitor that has failed due to age or wear and tear over time. There are many different types of capacitors available but they all serve one main function: to store energy in order to supply power for other components within your appliance such as motors, heating elements and lights etc… If your washing machine does not have a capacitor fitted then it will not be able to run properly or at all!
Why do Capacitors in Washing Machines Fail?
When a washing machine capacitor fails, the motor will not run. This is due to the fact that the capacitor stores energy and distributes it to the motor.
Corrosion – The most common cause of failure is corrosion on the contacts inside the capacitor. When this happens, it results in an open circuit which means that there is no flow of current between them.
This will cause your washing machine to stop working because it cannot generate enough power to spin at full speed or even turn on at all.
Heat – The heat generated by the motor can cause the dielectric fluid inside of the capacitor to evaporate. Once this happens, it will no longer be able to store electricity properly and can cause sparks or even a fire if not detected quickly enough!
Age – As capacitors age, they become less resistant to heat and voltage changes — which in turn causes them to fail prematurely.
Conclusion
If you have an older washing machine, it’s important to check the capacitors regularly and replace them as needed. Capacitors are relatively inexpensive and easy to find at most hardware stores.
If your washer is not working properly or has stopped working altogether, it could be due to a failed capacitor. Replacing the capacitor is a relatively simple and inexpensive fix that you can do yourself. However, if you are not comfortable working with electrical components, it’s always best to call a professional for help.